Write a program to implement stack using array in data structure
Introduction Stack
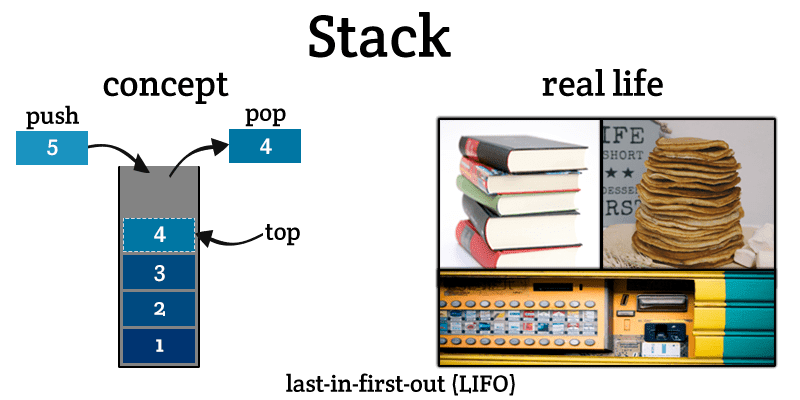
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out).
There are many real-life examples of a stack. Consider an example of plates stacked over one another in the canteen. The plate which is at the top is the first one to be removed, i.e. the plate which has been placed at the bottommost position remains in the stack for the longest period of time. So, it can be simply seen to follow LIFO(Last In First Out)/FILO(First In Last Out) order.
stack
stack operations Algorithm by using Array
1. PUSH:-When we insert an element in a stack then the operation is known as a push. If the stack is full then the overflow condition occurs.
arr[top]=i
2. POP:- When we delete an element from the stack, the operation is known as a pop. If the stack is empty means that no element exists in the stack, this state is known as an underflow state.
3.isEmpty:- It determines whether the stack is empty or not.
4. peek:- It returns the element at the given position.
stack implementation by using Array
import java.util.Scanner;
class stack {
int n=10;
int top=-1;
int a[] =new int[10];
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
void push()
{
if(top== (n-1))
{
System.out.println("stcak is overflow");
}
else
{
System.out.println("enter the number");
int i =sc.nextInt();
top=top+1;
a[top]=i;
System.out.println("item inseret"
}
}
void pop()
{
if(top== -1)
{
System.out.println("stcak is underflow");
}
else
{
top=top-1;
System.out.println("item delete"
}
}
void display()
{
for(int j=top; j>=0 ;j--)
{
System.out.println(a[j]
}
}
}
class stack_array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
stack s = new stack();
while(true)
{
System.out.println("\n \n \n \n")
System.out.println("\t \t 1 push")
System.out.println("\t \t 2 pop")
System.out.println("\t \t 3 display ")
System.out.println("\t \t 4 exit")
System.out.println("enter the choic"
int ch =sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1: s.push(); break;
case 2: s.pop(); break;
case 3: s.display(); break;
case 4: System.exit(1); break;
default: System.out.println("try again"
}
}
}
}
stack implementations ways
- how implement stack By using array
- how implement stack By using Linked list
- how implement stack By using stack class
Next Topic

No comments:
Post a Comment